はじめに
Dify API 拡張は API Endpoint としてアクセス可能な公開ネットワークアドレスを使用する必要があるため、API 拡張を公開ネットワークアドレスにデプロイする必要があります。 ここでは Cloudflare Workers を使用して API 拡張をデプロイします。 Example GitHub Repository をクローンします。このリポジトリには簡単な API 拡張が含まれており、これをベースに変更できます。wrangler.toml ファイルを開き、name と compatibility_date をアプリケーション名と互換性日付に変更します。
ここで注意が必要な設定は、vars 内の TOKEN です。Dify で API 拡張を追加する際に、この Token を入力する必要があります。セキュリティ上の理由から、Token としてランダムな文字列を使用することをお勧めします。ソースコードに直接 Token を書き込むのではなく、環境変数を使用して Token を渡すべきです。そのため、wrangler.toml をコードリポジトリにコミットしないでください。
src/index.ts でこの API 拡張のロジックを変更できます。この例は、サードパーティ API とのやり取り方法を示しています。
npm コマンドを直接使用して API 拡張をデプロイできます。
endpoint パスを忘れないでください。このパスの具体的な定義は src/index.ts で確認できます。
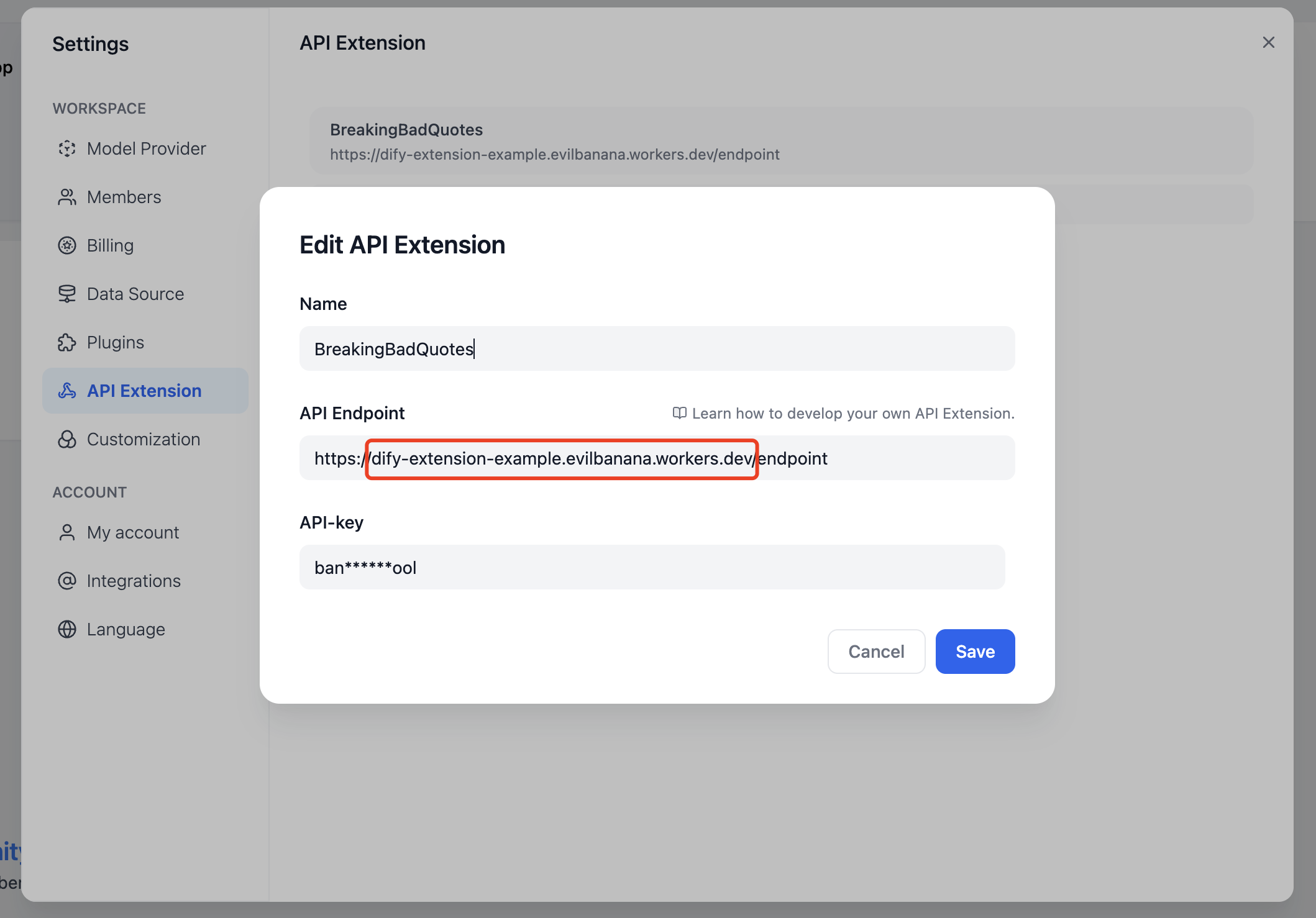 また、
また、npm run dev コマンドを使用してローカルにデプロイしてテストすることもできます。
Bearer Auth について
hono/bearer-auth パッケージを使用して Bearer 検証を実装しています。src/index.ts で c.env.TOKEN を使用して Token を取得できます。
パラメータ検証について
zod を使用してパラメータの型を定義しています。src/index.ts で zValidator を使用してパラメータを検証できます。const { point, params } = c.req.valid("json"); で検証済みパラメータを取得します。
ここでの point は 2 つの値しかないため、z.union を使用して定義しています。params はオプションのパラメータなので、z.optional を使用して定義しています。その中には inputs パラメータがあり、これは Record<string, any> 型です。この型は、キーが string で値が any のオブジェクトを表します。この型は任意のオブジェクトを表すことができます。src/index.ts で params?.inputs?.count を使用して count パラメータを取得できます。
Cloudflare Workers のログを取得
参考資料

